Toilet Overflowing but Not Clogged? Read This!
Toilet overflows can be a messy and frustrating experience for any homeowner. While it is common for an overflowing toilet to be the result of a clog in the drain, there are other potential reasons why a toilet might overflow without being clogged.
Understanding these causes is crucial to properly diagnose and address the issue, avoiding potential water damage and further complications. When I worked in maintenance at a property that had more than 250 toilets, I faced this very problem a number of times over the span of 10 years.
In this article, we will explore five possible reasons for a toilet overflowing without a clog, providing detailed information on each cause, why it happens, and how to fix the problem. By being aware of these potential issues, you can take the necessary steps to prevent toilet overflows and maintain a clean, functional, and stress-free bathroom environment.
Hopefully you won’t even need to call a handyman like myself to help you out, though I would always be glad to. Let’s get started!
Malfunctioning Fill Valve
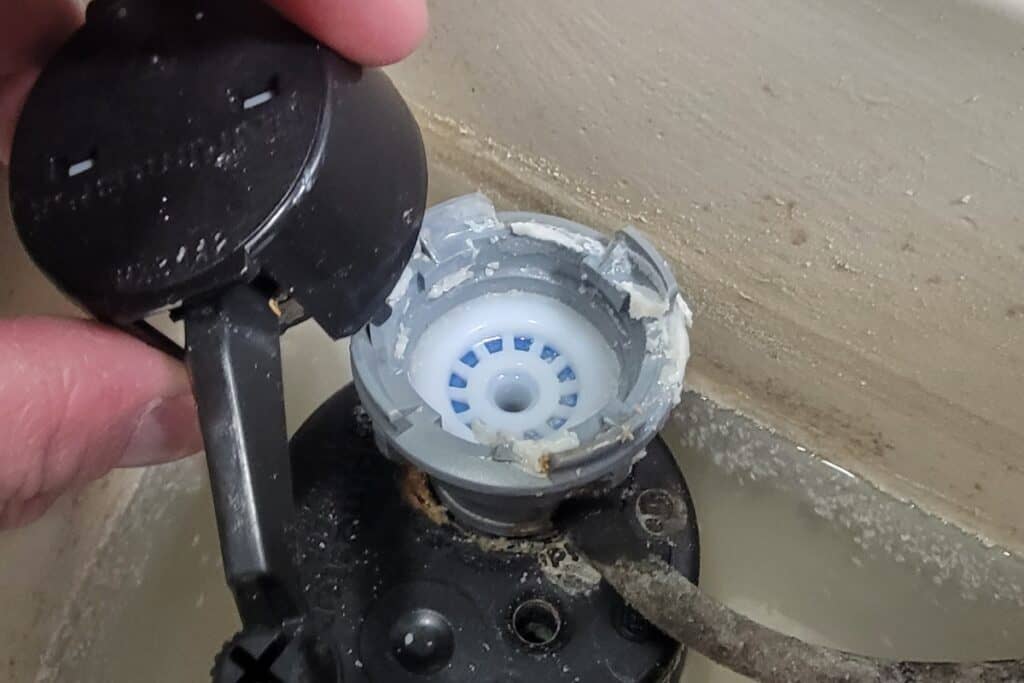
A malfunctioning fill valve can cause a toilet to overflow without being clogged. The fill valve is responsible for controlling the flow of water into the toilet tank after each flush. If it is damaged or not properly adjusted, it may continue to let water into the tank, causing the water level to rise until it overflows. A malfunctioning fill valve can waste a significant amount of water, leading to higher utility bills and potential water damage.
How to fix: Adjusting the fill valve is typically a simple fix that most homeowners can handle on their own. If the fill valve is damaged, you may need to replace it. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and adjustment.
As a general rule, follow these steps to replace a fill valve:
- Turn off the water supply to the toilet.
- Flush the toilet to empty the tank.
- Disconnect the water supply line from the fill valve.
- Unscrew and remove the old fill valve.
- Install the new fill valve according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Reconnect the water supply line.
- Turn on the water supply and adjust the fill valve as needed.
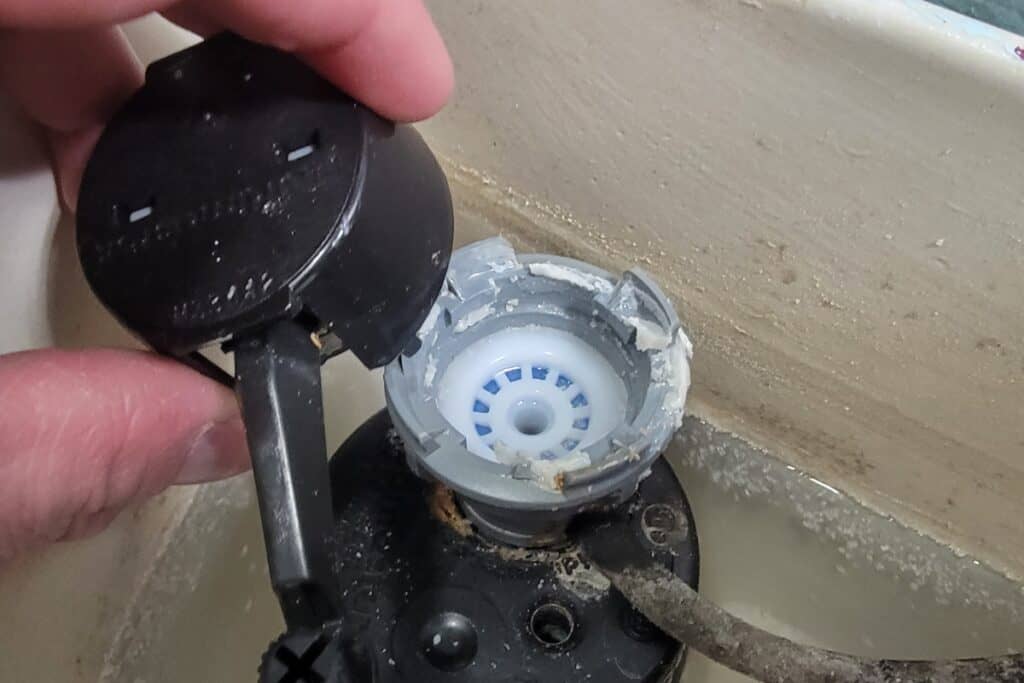

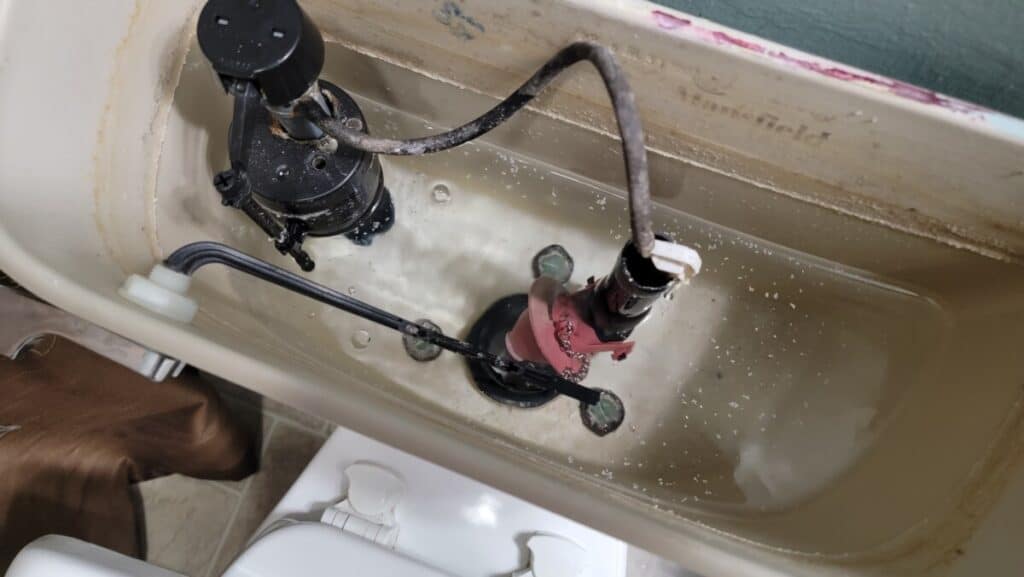
Faulty Flapper or Flush Valve
Another reason a toilet may overflow without being clogged is a faulty flapper or flush valve. The flapper is the rubber piece at the bottom of the toilet tank that lifts up to let water flow into the bowl during a flush. If the flapper doesn’t seal properly after a flush, water will continue to flow into the bowl, causing it to overflow. Similarly, a damaged flush valve can also prevent the flapper from sealing properly, leading to the same issue.
How to fix: Inspect the flapper and flush valve for damage or wear. Try cleaning it first by massaging it between your fingers to clean off any mineral deposits. If that doesn’t work, replace the flapper if necessary. Ensuring a proper seal between the flapper and the flush valve can prevent water from continuously flowing into the bowl and causing an overflow.
Here’s a general idea of how replace a flapper:
- Turn off the water supply to the toilet.
- Flush the toilet to empty the tank.
- Unhook the flapper chain from the flush handle lever.
- Remove the old flapper by unhooking it from the overflow tube.
- Install the new flapper and attach it to the overflow tube.
- Reattach the flapper chain to the flush handle lever.
- Turn on the water supply and test the flapper for proper operation.
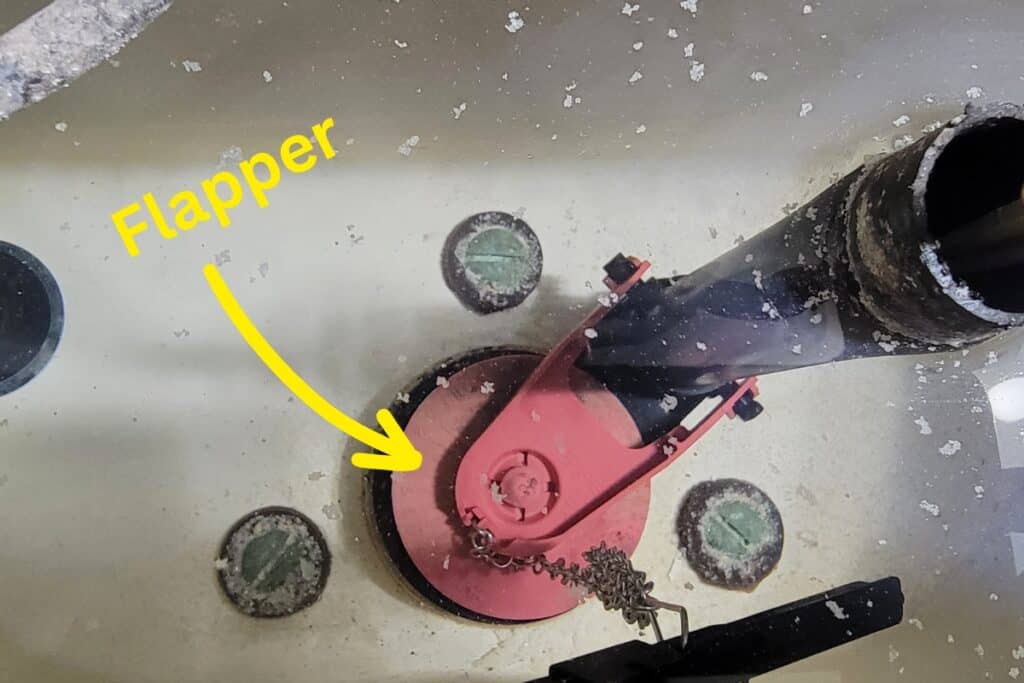

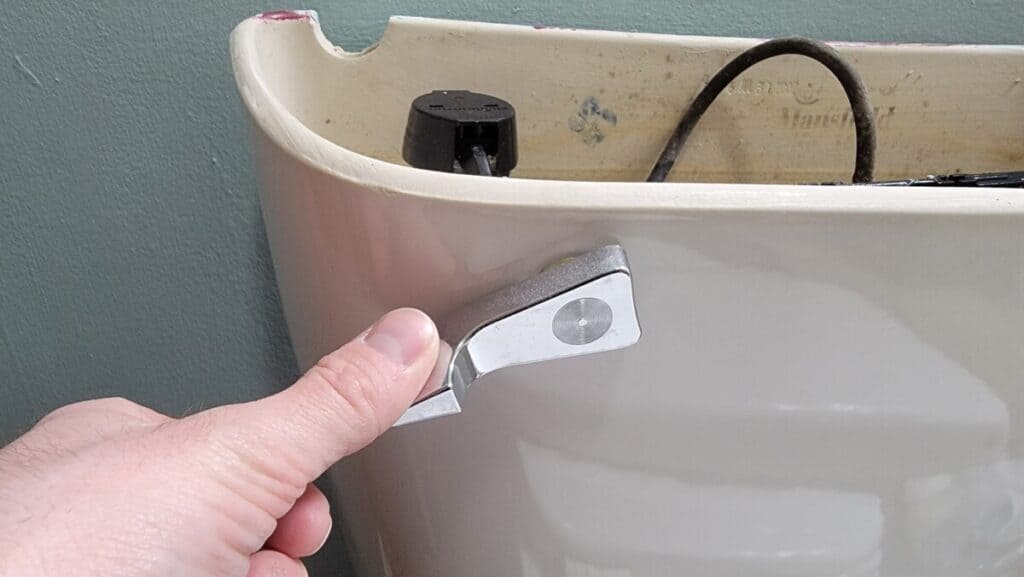
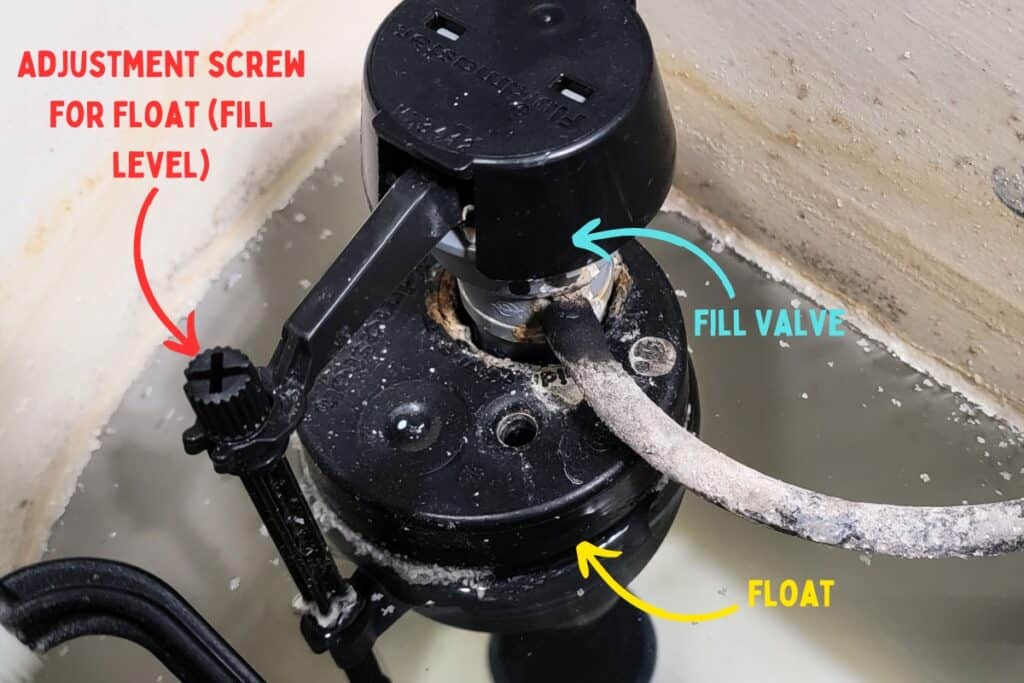
Improperly Adjusted Float
An improperly adjusted float can also cause a toilet to overflow. The float is a component inside the toilet tank that rises and falls with the water level, signaling the fill valve to shut off when the tank is full. If the float is set too high, the water level in the tank will be too high, which can cause an overflow.
How to fix: Adjust the float to the proper height to prevent overflows. This is typically a simple task that homeowners can handle themselves, but make sure to consult your toilet’s manual for specific instructions on adjusting the float.
How to Adjust a Float with an Adjustment Screw:
- Locate the adjustment screw on the float arm.
- Turn the screw clockwise to raise the water level or counterclockwise to lower it.
- Flush the toilet to check the water level and adjust as needed.
How to Adjust a Float with a Bendable Arm:
Only do this if the arm is made of metal. If it’s plastic, you cannot bend it, it will break. Plastic arms should have an adjustment screw.
- Gently bend the float arm up to raise the water level or down to lower it.
- Flush the toilet to check the water level and adjust as needed.
Blocked or Obstructed Vent Pipes
Blocked or obstructed vent pipes can lead to toilet overflows without a clog. Vent pipes allow sewer gases to escape and help maintain proper pressure in the plumbing system. If the vent pipe is blocked, the pressure can cause water to back up and overflow in the toilet.
How to fix: Clearing the obstruction in the vent pipe will typically resolve the issue. However, this task can be difficult for homeowners and may require the help of a professional plumber or trusted handyman.
How to Check and Clean a Vent Pipe:
- Locate the vent pipe on the roof of your home.
- Inspect the vent pipe for visible blockages, such as leaves, debris, or bird nests.
- Use a flashlight to look inside the vent pipe for any obstructions.
- If necessary, use a plumber’s snake or a long flexible brush to clean the vent pipe.
- If the vent pipe is still blocked or you are unsure of the issue, consider hiring a professional plumber to inspect and clean the vent pipe.
Sewer Line Issue
A sewer line issue can cause a toilet to overflow without being clogged. If the sewer line is blocked or damaged, it can prevent the proper flow of water and waste, causing water to back up into the toilet.
How to fix: In this case, you will likely need the help of a professional plumber to diagnose and repair the problem. Sewer line issues can be complex and require specialized tools and expertise to address properly.
Important Takeaways
While clogs are a common cause of toilet overflow, there are several other factors that can lead to this frustrating issue. By understanding the different reasons for toilet overflow and addressing them accordingly, you can help prevent this problem from occurring and maintain a well-functioning bathroom.
Regardless of why the toilet is overflowing, it’s a good idea to ensure your toilet’s base is properly sealed where it comes into contact with the floor. If it isn’t, then water can run underneath and become nearly impossible to remove which can damage the floors beneath or cause bacteria and odor to grow. Here’s a guide on how to take care of this if you haven’t sealed your toilet base already.
Remember to regularly inspect and maintain your toilet components, and don’t hesitate to call a professional plumber or trusted handyman if you’re unsure how to handle a particular issue. With the right knowledge and care, you can keep your toilet running smoothly and avoid unexpected overflows.







